Utimaco uTrust and CryptoServer integration in Kubernetes
ENTERPRISE
The Utimaco HSM sidecar container enables integrating the application container to a network-attached Utimaco uTrust and CryptoServer HSM. The following covers how to set up the integration in Kubernetes.
For more general information on the HSM integration with PKCS#11, see HSM Integration.
Prerequisites
Before using this container, you need the following:
A pre-installed Utimaco network-attached HSM (or Utimaco emulator for testing).
At least one PKCS#11 slot configured with soft authentication and a known passphrase.
Prepare HSM configuration
The HSM driver client needs to be configured to communicate with the Utimaco HSM. The configuration file cs_pkcs11_R3.cfg is shared with the HSM driver (sidecar) container as a Kubernetes ConfigMap.
Mandatory configuration: HSM server location
The configuration must define the HSM location using either:
A
[HSMCluster]section, orA
[CryptoServer]section (deprecated by Utimaco)
Only one of these sections may be present.
Typical configurations include:
[HSMCluster]
ClusterID = 0000
Devices = 192.168.8.101Using explicit port and IP:
CODE[HSMCluster] ClusterID = 0000 Devices = 3001@192.168.8.101Using domain name (must not contain hyphens):
CODE[HSMCluster] ClusterID = 0000 Devices = 4001@hsmdomainLegacy form, without ClusterID:
CODE[HSMCluster] Devices = 192.168.28.28Deprecated configuration using
[CryptoServer]:CODE[CryptoServer] Device = 3001@utimaco-emulator
For reference, the default ports are:
288 for netHSM
3001 for the Utimaco emulator
Example Kubernetes Manifest
The configuration supports several additional parameters such as logging, connection timeouts, session handling, and key-storage settings. Modify these as required for your environment.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: ejbca-utimaco-configmap
data:
cs_pkcs11_R3.cfg: |
[Global]
# Path to the logfile (name of logfile is attached by the API)
# For unix:
Logpath = /opt/utimaco
# Loglevel (0 = NONE; 1 = ERROR; 2 = WARNING; 3 = INFO; 4 = TRACE)
Logging = 0
# Maximum size of the logfile in bytes (file is rotated with a backupfile if full)
Logsize = 0
# Created/Generated keys are stored in an external or internal database
KeysExternal = false
# If true, every session establishes its own connection
SlotMultiSession = true
# Maximum number of slots that can be used
SlotCount = 10
# If true, leading zeroes of decryption operations will be kept
KeepLeadZeros = false
# Configures load balancing mode ( == 0 ) or failover mode ( > 0 )
# In failover mode, n specifies the interval in seconds after which a reconnection attempt to the failed CryptoServer is started.
FallbackInterval = 0
# Prevents expiring session after inactivity of 15 minutes
KeepAlive = false
# Timeout of the open connection command in ms
ConnectionTimeout = 5000
# Timeout of command execution in ms
CommandTimeout = 60000
# List of official PKCS#11 mechanisms which should be customized
#CustomMechanisms = { CKM_AES_CBC CKM_AES_ECB }
# Enforce thread-safety by using the operating system locking primitives
#ForceOSLocking = true
# The [HSMCluster] section replaces the deprecated [CryptoServer] section. For backwards-
# compatibility, a [CryptoServer] section can still be used, but it MUST NOT be mixed with
# [HSMCluster] sections.
[HSMCluster]
# Device specifier (here: local simulator)
Devices = 3001@127.0.0.1
# Device specifier (here: cluster of simulators)
#Devices = { 3001@127.0.0.1 3003@127.0.0.1 }
# Device specifier (here: cHSM on remote u.trust Anchor device - port = base port (4000) + cHSM slot (1))
#Devices = 4001@192.168.0.1
# Device specifier (here: remote device with IP address 192.168.0.1)
#Devices = 192.168.0.1
# Device specifier (here: cluster of remote devices - first as above, others using format <port>@<ip>)
#Devices = { 192.168.0.1 288@192.168.0.2 4001@192.168.0.3 }
#[CryptoServer]
# Device specifier (here: CryptoServer is internal PCI device)
# For unix:
#Device = /dev/cs2
# For windows:
#Device = PCI:0
#[CryptoServer]
# Device specifier (here: CryptoServer is CSLAN with IP address 192.168.0.1)
#Device = 3001@utimaco-emulator
#[CryptoServer]
# Device specifier (here: CryptoServer is logical failover device of CSLANs with IP address 192.168.0.2 and IP address 192.168.0.3)
#Device = { 192.168.0.2 192.168.0.3 }
#[CryptoServer]
# Device specifier Simulator
#Device = { 3001@127.0.0.1 3003@127.0.0.1 }
#[Slot]
# Slotsection for slot with number 0
#SlotNumber = 0
#[KeyStorage]
# Legacy SDB file
#KeyStorageType = Legacy
# Path to the external keystore
# If KeyStore is defined the external keystore will be created and used at the defined location
# For unix:
#KeyStore = /tmp/P11.pks
# For windows:
#KeyStore = C:/ProgramData/Utimaco/PKCS11_R3/P11.pks
# Database via ODBC
#KeyStorageType = odbc
#KeyStorageConfig = "DSN=PSQL Ucapi External Storage"Configure Deployment
The following provides an example of customizing the deployment using Helm. The hsm section is configured to use the utimaco HSM with the ConfigMap just created.
Note that the Helm chart values file values.yaml describes an example test deployment and does not include:
Database connection.
Configured
imagePullSecretsthat may be required.TLS connection required after the deployment and creation of the CAs.
Ensure that the deployment is allowed an Egress to the physical HSM.
ejbca:
# signserver:
env:
TLS_SETUP_ENABLED: "later"
LOG_AUDIT_TO_DB: true
#################### HSM configuration - start ####################
hsm:
enabled: true
utimaco:
enabled: true
hsmConfigurationConfigMap: "ejbca-utimaco-configmap"
#################### HSM configuration - end ####################
# needed to make softhsm volume mount to work
podSecurityContext:
fsGroup: 10001
ingress:
enabled: true
className: "nginx"
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-verify-client: "optional_no_ca"
#nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-secret: "playground/ejbca-ingress-trust-secret"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-pass-certificate-to-upstream: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-verify-depth: "1"
hosts:
- host: "ejbcaca.testdomain.se"
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
#tls:
# - hosts:
# - "ejbcaca.testdomain.se"
# secretName: ingress-nginx-credential-secret-ca Create and verify HSM crypto token
To create a crypto token and then test the HSM key, do the following:
In the EJBCA menu, click CA Functions > Crypto Tokens.
Click Create new and specify the following on the New Crypto Token page:
Name: Specify a name for the crypto token.
Type: Select PKCS#11 NG.
Auto-activation: Select use to allow EJBCA to save the password and reapply it after a restart so that the CA is always available.
For PKCS#11 : Reference Type, select Slot/Token Label.
For PKCS#11 : Reference, select one of the listed slots available in the HSM.
Authentication Code: Enter a password for auto-activation, same as provided for the slot or token in the HSM.
Click Save to create the crypto token.
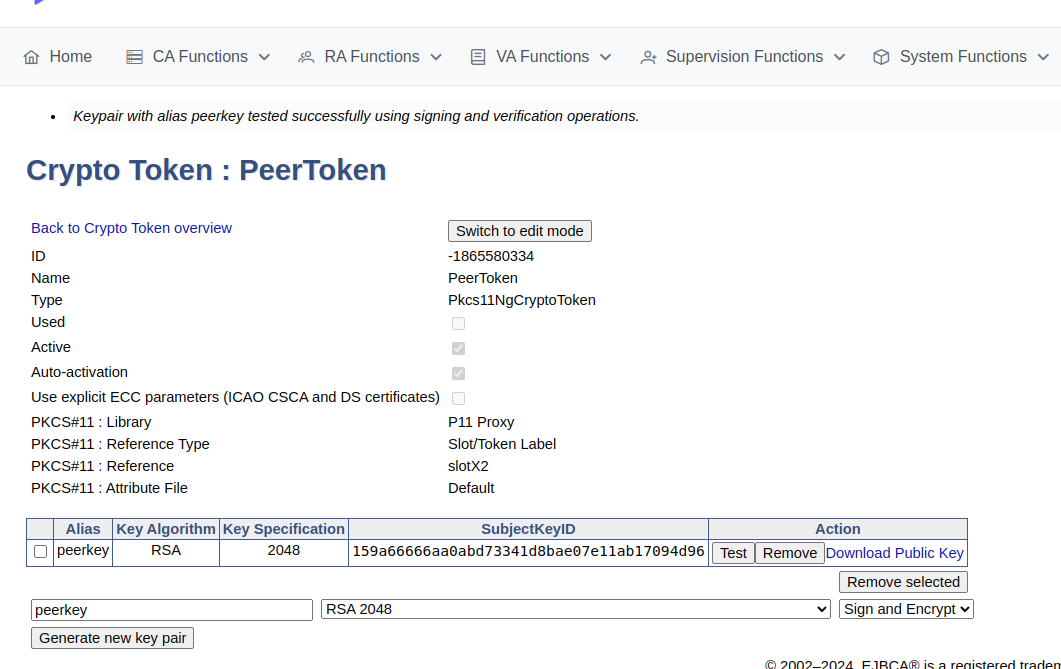
Once created, you can generate new key pairs or view any existing key pairs on the HSM.
To verify that communication with the HSM is functional, select the crypto token and click Test.
Advanced deployments
The EJBCA Enterprise configuration export/import tool EJBCA ConfigDump allows you to deploy EJBCA with automation. For information on deploying EJBCA with automation, using a soft HSM integration suitable for testing, see Deploy EJBCA as CA with automation with SoftHSM2.
Utimaco HSM installations can also be automated using the EJBCA ConfigDump tool. For information on how to configure the tool in Kubernetes, see EJBCA Configdump in Kubernetes.
The following provides example deployment artifacts:
For an example Kubernetes ConfigMap with ejbca-ca-init-configmap.yaml
HSM configurations
ConfigDump resources
(Optional) Script executed to create key pair during EJBCA installation
Helm chart values file (values.yaml): values-ca-full-doc.yaml
